Introduction
The rapid development of electronic products results in a significant need for either upgrading existing electronics production lines (EPLs) or designing newEPLs. Changes in product orders also lead to a frequent reconfiguration of electronics production lines. However, due to unreasonable design, many EPLs fail to meet the initial objective. This recommended practice addresses a preferred technique to help practitioners efficiently design a high-performance EPL.
Overview of the Standard
This recommended practice provides techniques for the variant design of electronics production lines. The techniques covered include requirements documentation, production line remodeling, variant design procedures, iterative design patterns, and results evaluation. This recommended practice may be useful for computer-aided design software suppliers, simulation software suppliers, information system suppliers, manufacturers, industrial control system suppliers, and equipment suppliers.
Key Features and Benefits
This recommended practice includes structure design, behavior planning, control architecture design, and performance optimization. It recommends customized design and implementation plans of EPL to meet the differentiated needs of manufacturers, such as site space constraints, capacity goals, cost control, individualized manufacturing process, and integration of legacy equipment. This recommended practice helps practitioners efficiently design a high-performance EPL.
Adoption and Impact
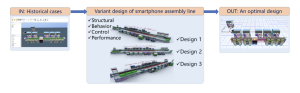
This recommended practice considers the variant design of a smartphone assembly line as a case study. The design schemes are developed quickly as variations of the smartphone assembly line are unexceptionally based on individualized needs for the site, legacy equipment, and capacity expectations. The physical structure of the whole production line and the performance of the modification scheme are different, depending on individualized requirements. Designers could choose different design schemes according to specific needs. This case study shows that the recommended practice has improved the manufacturer’s design capability of the production line.
Future Developments
The working group, which is managed by IEEE Computer Society Smart Manufacturing Standards Committee, identified three future research directions of the production line design, including typical reference models of EPL, concept design of AIGC-driven production line, and multi-disciplinary integration and cross-dimensional production line design.
Conclusion
This recommended practice provides techniques for the variant design of electronics production lines. The techniques covered include requirements documentation, production line remodeling, variant design procedures, iterative design patterns, and results evaluation. This recommended practice may be useful for computer-aided design software suppliers, simulation software suppliers, information system suppliers, manufacturers, industrial control system suppliers, and equipment suppliers. This case study shows that the recommended practice has improved the manufacturer’s design capability of the production line.
Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10707151
Disclaimer: The authors are completely responsible for the content of this article. The opinions expressed are their own and do not represent IEEE’s position nor that of the Computer Society nor its Leadership.